Typhoon Formation Shifts Closer to Shorelines Amid Climate Change
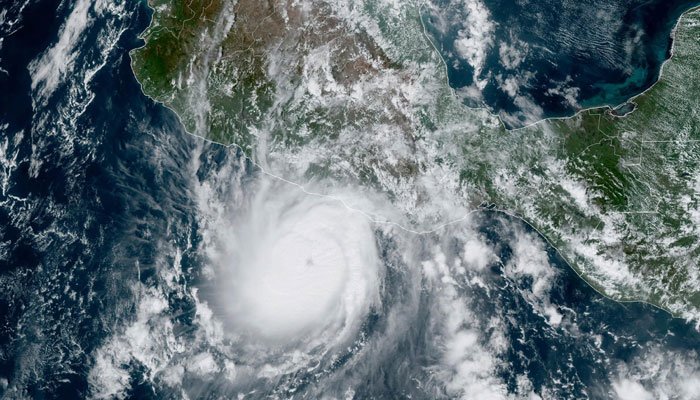
A recent study reveals that typhoons are forming closer to coastlines, a trend scientists attribute to climate change. This shift raises concerns about increased risks to coastal communities.
Researchers explain that warmer ocean temperatures and shifting atmospheric patterns cause typhoons to develop and intensify nearer to land. Consequently, this phenomenon reduces the warning time for residents and authorities to prepare for these powerful storms. Traditionally, typhoons had more time to build up over open waters before making landfall. However, this new pattern poses a significant threat to densely populated coastal areas.
The study, which analyzed data from the past several decades, highlights a clear trend of typhoons originating closer to shore. This shift is particularly noticeable in regions like the Western Pacific, where typhoons frequently occur. Scientists warn that as climate change continues to alter weather patterns, the frequency and intensity of these storms could increase, further endangering coastal populations.
Meteorologists and climate experts urge for improved forecasting models and enhanced infrastructure resilience in response to these findings. They emphasize the need for better emergency preparedness and response strategies, especially in vulnerable coastal regions. Consequently, governments and local authorities must invest in robust systems to mitigate the impacts of these increasingly common weather events.
More from wakopedia: Seoul Court Issues Arrest Warrant in Spy Leak Case
This study adds to the growing body of evidence linking climate change to more frequent and severe weather phenomena. As global temperatures rise, the effects on storm patterns and behaviors become more pronounced. Therefore, urgent action is needed to protect communities and infrastructure.
The implications of this research are significant, underscoring the urgency of international cooperation in combating climate change. By reducing greenhouse gas emissions and implementing sustainable practices, there is hope to mitigate some of the adverse effects and protect vulnerable populations from the escalating threats posed by typhoons and other extreme weather events.